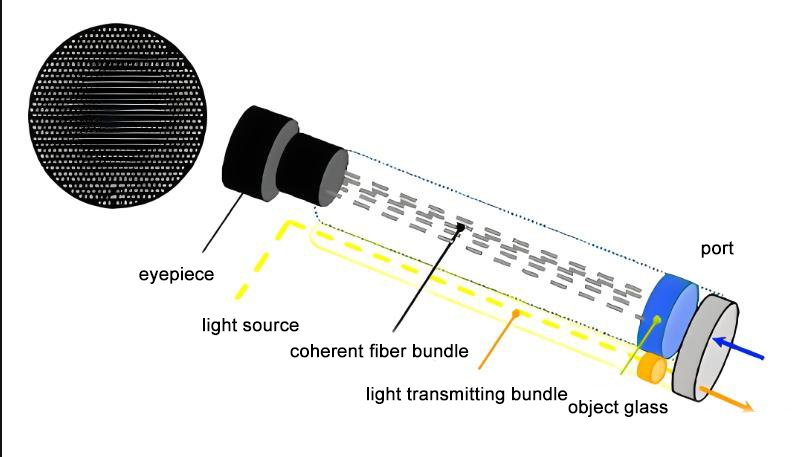
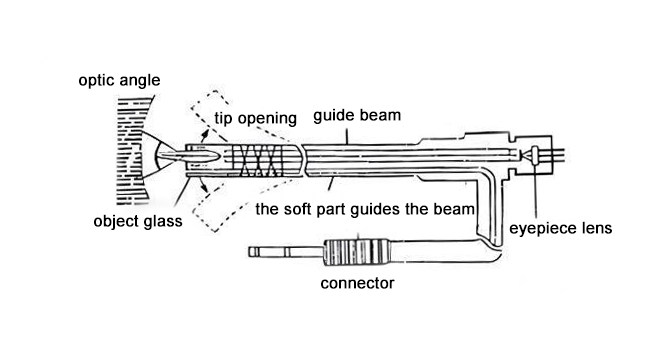
Industrial optical fiber endoscope is a kind of remote visual inspection equipment, with fine diameter, flexible characteristics, mostly used for some narrow curved test piece internal inspection, such as: turbine, small diameter process pipeline, aircraft fuselage, boiler pipeline maintenance, easy to use, is widely used. Understanding the imaging principles of industrial fiber optic endoscope can help to buy good products. Industrial fiber optic endoscopes often consof the objective lens, the mirror tube, the control unit, and the eyepiece. The guide beam providing lighting and the guide fiber optic beam responsible for transmission are all running through the mirror tube. The imaging core of optical fiber mirror lies in the optical fiber beam, and its imaging principle can be understood from the perspective of local single optical fiber and overall optical beam.
The imaging principle of industrial fiber optic endoscopy is based on a combination of optical and fiber optic technology, which allows the transmission of images through optical fibers, enabling visual detection in environments that are difficult to observe directly. This technology is widely used in aviation, automobile, electric power, chemical industry and other fields, providing a convenient and efficient means for the internal detection and maintenance of industrial equipment.
First, let's take a look at the basic structure and characteristics of the optical fiber. The optical fiber consists of three parts: fiber core, cladding and coating. The core is the core part of the optical fiber that transmits the optical signal; the cladding protects the optical signal and prevents its leakage; the coating is the outermost protective layer, increasing the durability and flexibility of the fiber. The characteristics of optical fiber include low loss, high bandwidth, and strong anti-interference ability, which makes optical fiber an ideal choice for long-distance, high-speed, and large-capacity data transmission.
In industrial optical fiber endoscopes, optical fibers are used to transmit light signals reflected back from the inside of the device. The probe portion of the endoscope is usually equipped with one or more fiber beams that introduce light signals from the external light source into the device and collect light signals reflected back from the inside of the device. These optical signals are transmitted to the viewing end through the fiber beam, which is then converted into a visual image through the imaging system.
At the core of the imaging system is the image sensor, which converts the received optical signal into an electrical signal, which is then processed through an electronic amplifier and finally output to the display. Depending on the type of sensor, the imaging system can be divided into two types: a charge-coupled device (CCD) sensor, and the other is a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) sensor. Both sensors have advantages and disadvantages, but both achieve high-quality image output.
In addition to the imaging system, industrial fiber-optic endoscopes require an optical system to focus and adjust the light. The optical system includes components such as an objective, an eyepiece and a focusing mechanism, which together ensure that the light can be accurately focused on the sensor to obtain a clear, accurate image.
In practical application, industrial optical fiber optic endoscope also needs to consider the influence of environmental factors. For example, the imaging quality of an endoscope may be affected in harsh environments such as high temperature, high humidity, and strong electromagnetic interference. Therefore, the design needs to take the corresponding protective measures, such as the use of high temperature, moisture, anti-interference optical fiber and sensors, to ensure that the endoscope can work normally in various environments.
In addition, the industrial fiber-optic endoscope also needs to consider the problem of image processing. Because the transmission process may be affected by noise, distortion and other factors, it is necessary to pre-processing, enhancement and recovery of the received images to improve the clarity and contrast of the image. These image processing technologies include filtering, denoising, enhancement, segmentation, which can help us to better identify and analyze the information in the image.
In conclusion, the imaging principle of industrial fiber optic endoscope is based on the combination of optical and fiber optic technology, through which images are transmitted through optical fibers and processed by the imaging system to obtain visual images. In practical applications, the influence of environmental factors and the problem of image processing are considered to ensure that the endoscope works properly and output high-quality images. With the continuous development of technology, industrial fiber optic endoscope will be applied and promoted in more fields.