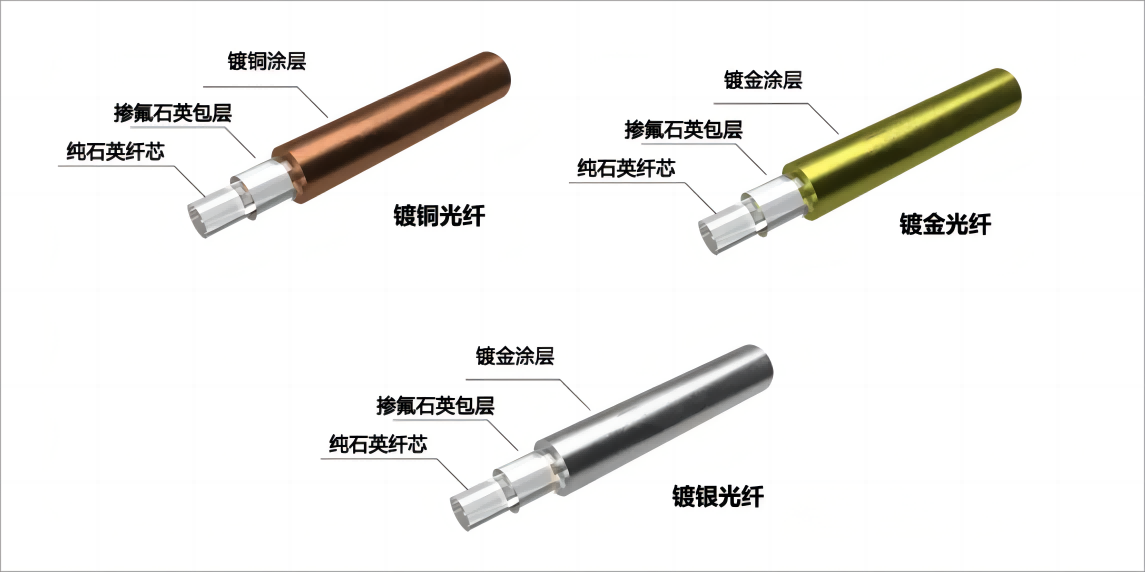
In environments above 400°C, organic materials used for coatings quickly undergo thermal oxidation aging, resulting in the loss of protection for the fiber and rendering it unusable. To enable normal operation at higher temperatures, high-temperature resistant metal materials (aluminum/copper/gold) are tightly wrapped around the bare fiber.
Benefits of using high-temperature resistant metals:
Lower coefficient of thermal expansion (similar to the fiber's coefficient)
Corrosion resistance
Good fatigue resistance, water resistance, and hydrogen resistance
High mechanical strength
Extreme high and low-temperature adaptability
Weldability
Using aluminum extends the temperature range from -269°C to +400°C, while copper extends it from -269°C to +600°C. Gold can withstand temperatures from -269°C to +700°C.
This type of fiber is used for ultra-longevity in harsh external environments and can also be used as components in electronic circuits. However, due to its complex manufacturing process and high cost, it is often only used in short segments where necessary.
Note: The metal coating process is complex and has very low production efficiency. Stripping the metal coating cannot be done with wire strippers and requires methods such as heat-sulfuric acid fusion or nitric acid for stripping.
The introduction above covers the three types of fiber metal coating materials. Quartz fiber is widely used in communication and non-communication fields due to its wide spectral range and low loss. However, it is necessary to select fibers with different coating materials based on the requirements of different applications, environments, and sectors.