It is well known that the optical fiber in the general sense is composed of a fiber core, cladding layer and coating layer. Among them, the fiber core, cladding determine its optical characteristics, generally with molten quartz in the environment of 2000℃ pull down, high temperature performance naturally need not say much. In the process of quartz glass pull, its surface will inevitably leave subtle cracks, used by a kinds of environmental stress, crack may rapidly expand and even break, so in the first time to help it put on a layer of sheath —— coating layer, to greatly improve its mechanical characteristics, make it more bending more tensile.
The coating material is mainly silicone or acrylic resin, which is attached to the bare fiber by thermal curing or UV curing process. But whether silicone resin or acrylic resin, the use environment is less than 180℃, above which temperature these materials will decompose and fail. In the petrochemical / aerospace / laser processing and other special industries, higher requirements are put forward for the high temperature characteristics of optical fiber, so the temperature limit of the coating layer can be broken, and the application scenario of optical fiber can be greatly expanded.
The significance of high temperature resistant fiber is that it can maintain stable transmission performance in extreme high temperature environment, and solves the problem that conventional fiber is easy to fail under high temperature conditions. The emergence of this fiber has greatly expanded the application field of fiber communication, especially in those scenarios that require long time to work in high temperature environment, such as petrochemical, power, metallurgy, automotive, aerospace and other industries.
It is understood that at domestic and foreign, the application scenario of high temperature resistant optical fiber is very wide. In the exploitation of oil and natural gas, the oil well temperature measuring optical cable needs to be able to withstand the underground high temperature and high pressure environment, and then it is necessary to use the high temperature resistant optical fiber. In thermal power generation, the real-time monitoring of boiler temperature and pressure also requires the stable transmission of high-temperature resistant optical fiber. In addition, in the automotive industry, high-temperature resistant optical fibers are used in on-board communication and entertainment systems to ensure the stable transmission of information in high-temperature engine and exhaust system environments. In the field of aerospace, the high temperature resistance performance of communication equipment is extremely high. The application of high temperature resistance optical fiber can improve the reliability and stability of communication equipment in high temperature environment.
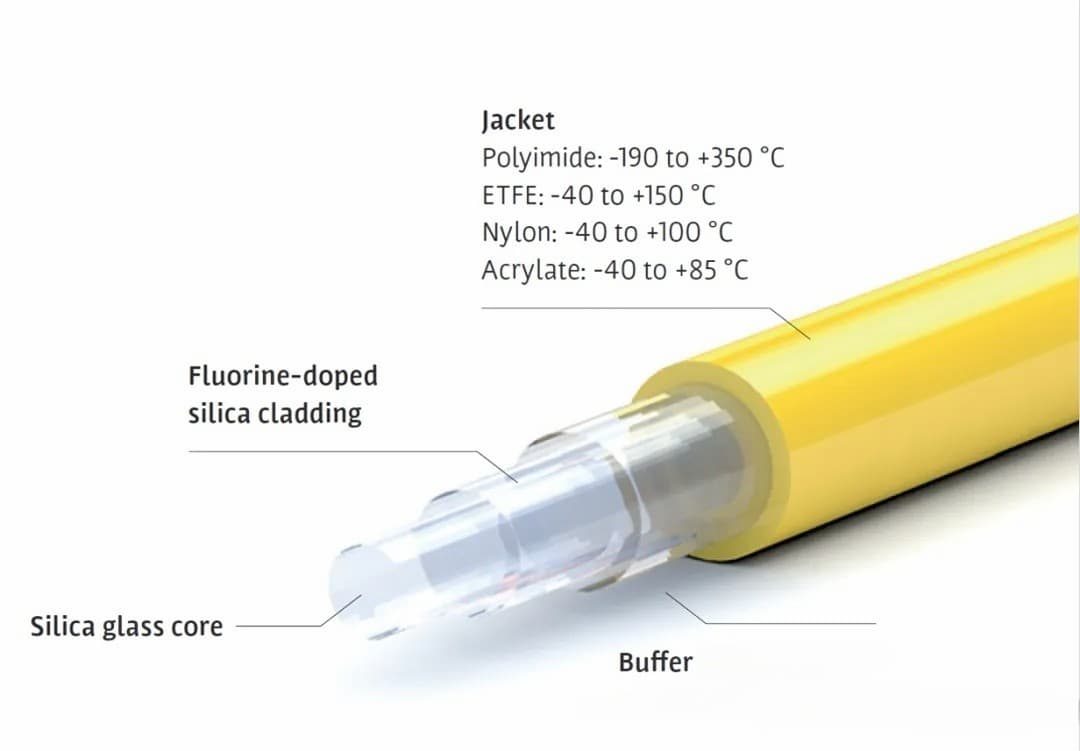

Polyimide (Polyimide, PI), with an excellent temperature range of-190℃ ~ + 385℃, has penetrated into every aspect of our lives since DuPont was first commoditized in 1961. For example, the flexible circuit board (FPC), often used in electronic products, is 280℃ lead-free welding and is made of polyimide; it is also made into fabric for firefighters, astronauts, and racers.
The key to polyimide's high temperature resistance lies in its unique molecular structure. Polyimide molecules contain multiple benzene rings and conjugated bonds, making their molecular structure relatively rigid. At the same time, the covalent bond between the acyl group in the molecule and the nitrogen atoms is very strong, and this structure gives the polyimide excellent thermal stability.

The thermal decomposition temperature of polyimide is very high, some specific types of polyimide, such as polyphenyltriazine dimethimide (BPDA-PDA), its thermal decomposition temperature can even reach more than 600℃. This high thermal stability makes the polyimide an ideal coating material for making high-temperature resistant optical fibers, greatly increasing the application temperature range of the optical fibers. Optical fibers made of such materials are often called PI optical fibers.
Mass production of PI optical fiber is not suitable. First, optical fiber coating generally requires two coatings inside and outside, and inner coating has low modulus for buffer, and outer coating has high modulus for protection. While the polyimide does not appear to have such properties. It is common to either use polyimide as a single coating at its mechanical properties, internal or conventional acrylic resin and polyimide to resist instantaneous high and low temperatures. Secondly, the curing process of polyimide is not too mature and cannot be as uniformly and firmly attached as traditional coatings.
The process of plating polyimides on the outer surface of the fiber usually involves the coating technique. A common method is to use a dip-coating method. In this process, the bare fiber region of the fiber is slowly immersed in the polyimide solution, ensuring that the fiber makes full contact with the solution. The fiber was then pulled out from the solution at a certain speed to control the thickness of the coating. The coated optical fibers need to be cured at lower ambient temperatures to volatilize the solvent and avoid creating bubbles during subsequent heating. Finally, the fiber will be placed in a high-temperature box for heating, making the polyimide coating more tightly attached to the fiber surface.
In theory, 385℃ is the upper temperature limit of the polyimide, regardless of higher temperatures. High temperature resistant metal coated fiber, by coating the surface of the bare fiber with a layer of high temperature resistant metal material, such as aluminum, copper or gold, to improve the performance of the fiber in high temperature environment. This fiber performs well at extreme temperature conditions and has excellent resistance to chemical corrosion and mechanical bending.
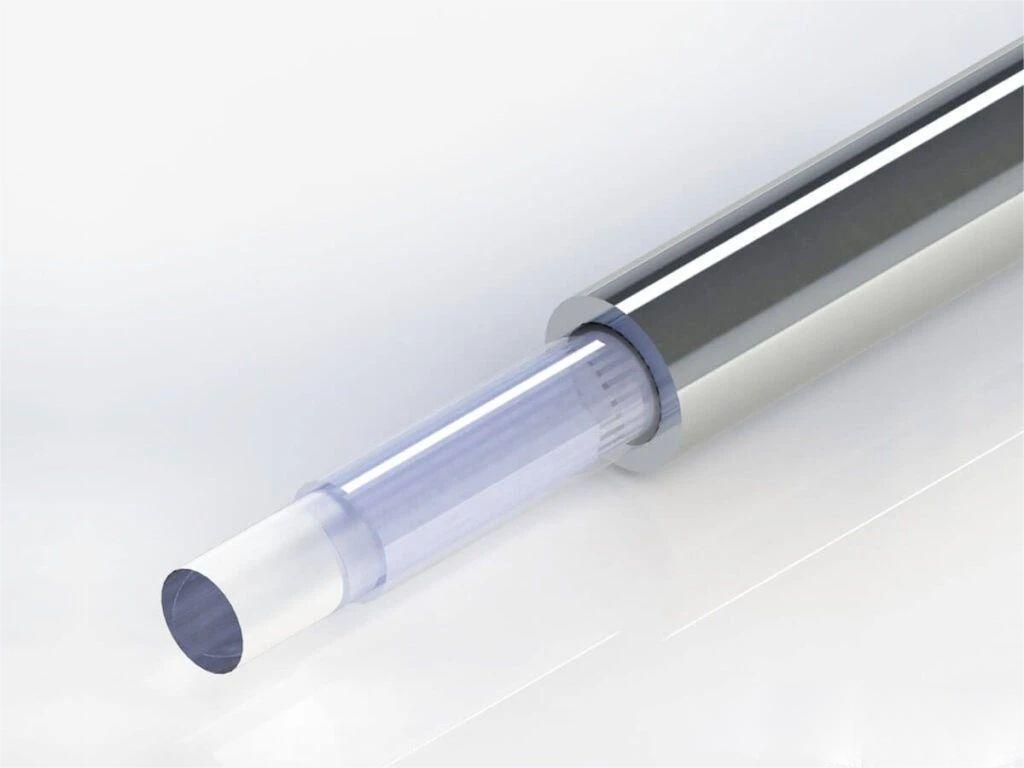

High temperature-resistant metal-coated optical fibers are widely used in areas that need to withstand high temperature and corrosive environments. For example, metal-coated optical fibers all play an important role in nuclear radiation, high-energy and strong laser transmission, welded fiber beams, and medical applications. In addition, in the field of high temperature sensing fiber, it can be used as turbine sensing fiber, oil and gas well fiber, engine sensing fiber, etc., to withstand the work demand in high temperature environment. Metal optical fibers are also often used as gas-tight optical fibers.
